Introduction
Screen or GNU Screen is a terminal multiplexer. In other words, it means that you can start a screen session and then open any number of windows (virtual terminals) inside that session. Processes running in Screen will continue to run when their window is not visible even if you get disconnected.
Install Linux Screen on Ubuntu or Debian
sudo apt update
sudo apt install screen
Starting Screen
screen
If you run multiple screen, set session name for screen, easy to control
screen -S [session_name]
Some most commands for manage Screen
Ctrl+acCreate a new window (with shell)Ctrl+a"List all windowCtrl+a0Switch to window 0 (by number )Ctrl+aARename the current windowCtrl+aSSplit current region horizontally into two regionsCtrl+a|Split current region vertically into two regionsCtrl+atabSwitch the input focus to the next regionCtrl+aCtrl+aToggle between the current and previous regionCtrl+aQClose all regions but the current oneCtrl+aXClose the current region
Check and find Screen
screen -ls
Kill Screen
screen -XS [session # you want to quit] quit
(-X = Execute command, -S session PID to execute on)
Example:
screen -XS 20411 quitReattach to a Linux Screen
To reume your screen session use the following command:
screen -r
Detach from Linux Screen Session
You can detach from the screen session at any time:
ctrl+a d
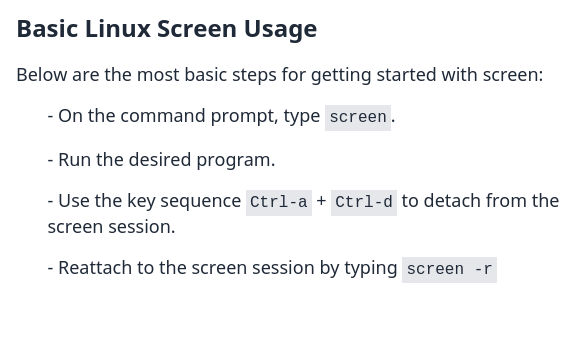
Basic Linux Screen Usage
Below are the most basic steps for getting started with screen:
- On the command prompt, type screen.
- Run the desired program.
- Use the key sequence to Ctrl-a + d detach from the screen session.
- Reattach to the screen session by typing screen -r
.^^